In order to make the mBot stop when he finds an obstacle, we use the ultrasound sensor, placed in the eyes of the robot: one eye is the ultrasound transmitter (indicated by the letter T), whereas the other one is the receiver (indicated with the letter R).
In order to make the mBot stop when he finds an obstacle, we use the ultrasound sensor, placed in the eyes of the robot: one eye is the ultrasound transmitter (indicated by the letter T), whereas the other one is the receiver (indicated with the letter R).
The ultrasound sensor allows us to let mBot know the distance of the object in front of him, without touching it. The transmitter emits an ultrasound signal, which is reflected by the object and goes back to the receiver. By measuring the interval between the instant in which the signal started, and the one in which the reflected signal was received – knowing that sound propagates at a speed of about 344 metres per second (in the air and at room temperature) – the distance of the robot from the object is calculated.
mBot can measure the distance in centimetres with a precision of 1 cm and a maximum distance of 400 cm.
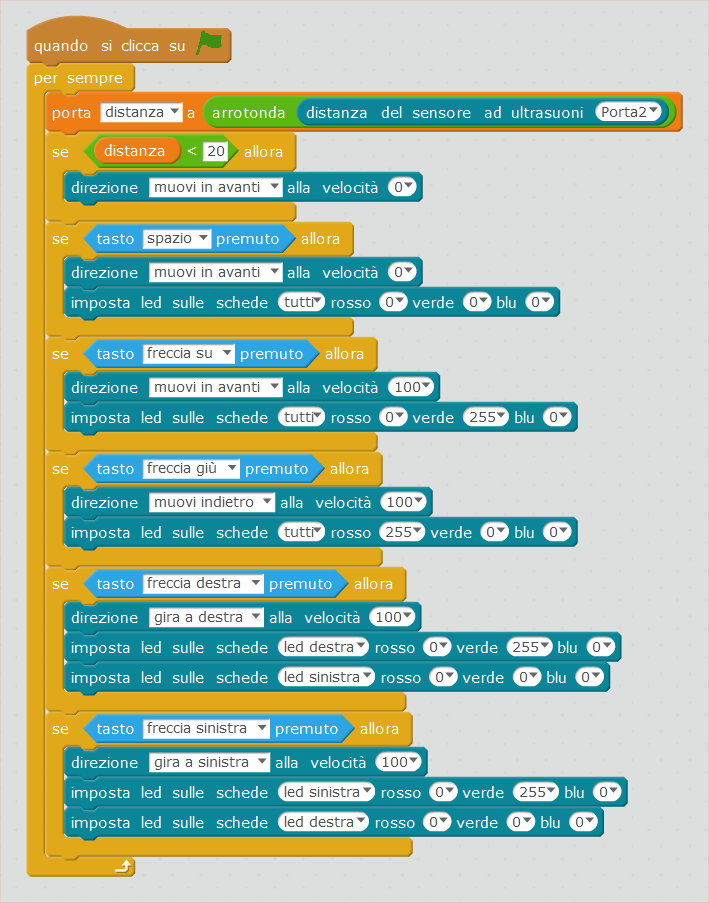
First of all, we define a variable Distance, to which we assign the value detected by the ultrasound sensor.
In the command distance of the ultrasound sensor, we need to select a port. All entries on the robot are marked with a number from 1 to 4: we should understand to which port the flat cable coming from the mBot eyes is connected, and select the corresponding port in the drop-down menu.
In order to make sure that the distance is shown in real time, we should insert the variable setting inside a forever loop.
At this point, in the display appeared on the stage with the creation of the variable you can read the distance of the object in front of mBot, if the obstacle is at a distance of less than 4 metres. You will see that many digits appear after the comma, which change quickly if the robot moves. If you prefer, you can insert the command distance of the ultrasound sensor inside the command round up, so as to see the distance as a whole number.
With the following code, you can pilot the robot with the keyboard arrows, so that he will stop of his own accord when he comes across an object, at less than 2 centimetres.